
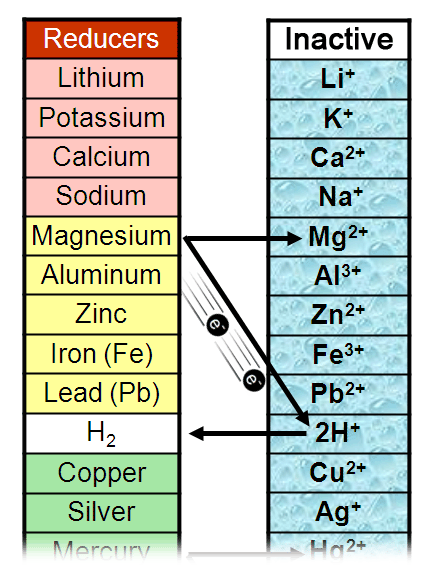
For example, reactive metals are added to the solution of less reactive metals for extraction purposes. Metals displacement reactionsĪctivity series of metals can be used to predict metal displacement. For example, at room temperature zinc does not react with water but above 50✬ it reacts, and hydrogen bubbles are witnessed. On going down the activity series, the tendency of metals to react decreases. The topmost metals react vigorously with water to liberate hydrogen gas. The reaction of metals with water can be predicted with activity series of metals.

Therefore it can replace the copper from the CuSo 4 solution and become Zn 2+. This means that the metals with more than one electron in the outermost shell are more reactive than the ones having just one electron.įor example, zinc is more reactive than copper. The reason is the additional shell makes farther the leaving electron. The activity of alkali metals increases down the group. Alkali metals have one outermost electron so they can lose their electron to gain a stable configuration. Some metals are more reactive than others because of their electronic configuration. The activity of metals is defined by their ability to lose electrons and become ions. Applications and uses of activity series of metals.The significant features of the activity series.It is important to note that this activity series is not absolute and can vary slightly depending on the specific conditions of the reaction. Moreover, this activity series describes the loss of electrons (oxidation potential), corrosive nature, and energy required for metal extraction processes from the ores. The more reactive metal will displace the less reactive metal from a compound.

For example, if a metal higher in the activity series reacts with a compound containing a metal lower in the series, a single displacement reaction will occur. The activity series can help predict if a single displacement reaction will occur. The more reactive a metal is, the more likely it is to lose electrons and form a positive ion. The reactivity of these metals is usually determined by their ability to form positive ions. In the series, elements on the top are more reactive than those at the bottom. Activity series or reactivity series of metals explain certain properties of metals, mainly the reactivity of metals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
